Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase acid like 3B (SMPDL3b) regulates Perilipin5 (PLIN5) expression and mediates lipid droplet formation


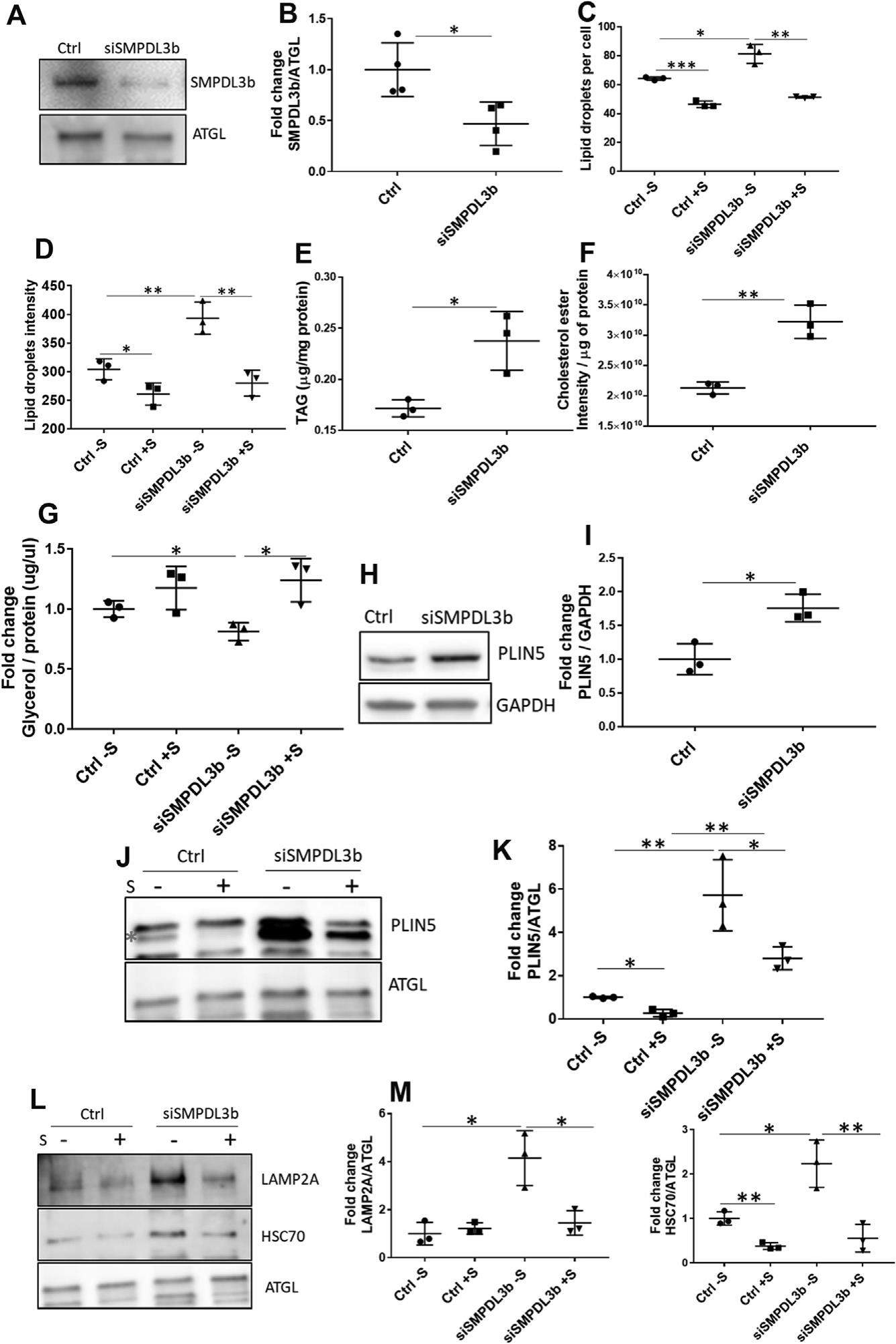
Lipid droplets (LDs) are lipid storage organelles with a central hydrophobic core of neutral lipids that is enclosed in a monolayer of phospholipids. Though the storage of lipids, mainly cholesterol and triglycerides, was thought to be the primary function of LDs, studies have shown that they have important functions in maintaining lipid homeostasis and modulating various signaling pathways. Abnormal lipid accumulation has been recognized as a key feature in several human diseases such as obesity, diabetes, cancer, neurological diseases, cardiovascular diseases, insulin resistance, liver diseases and kidney diseases. LDs play an important role in innate immunity, in the fight against infections, and in the replication of SARS-CoV-2. Hence a tight regulation of LD metabolism is essential for proper functioning of a cell. We previously reported an important role for LD accumulation and the progression of kidney diseases, including diabetic kidney disease and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). In FSGS, we found that glomerular LD accumulation coincided with decreased expression of sphingomyelinase phosphodiesterase like 3b (SMPDL3b), an enzyme we showed to regulate ceramide-1-phosphate levels in podocytes, suggesting a role for SMPDL3b in sphingolipid metabolism. However, if SMPDL3b regulates LD homeostasis is unknown. The present study was aimed at determining if SMPDL3b regulates LD homeostasis in immortalized human podocytes, which are terminally differentiated cells that have a key role in the glomerular filtration barrier. We found that SMPDL3b is localized to LDs and that reduced expression of SMPDL3b is associated with an increase in the number of LDs, increased levels of triglycerides (TAG) and cholesterol esters, increased uptake of fatty acids and decreased lipolysis. Reduced expression of SMPDL3b leads to an increase in PLIN5, heat shock cognate protein (HSC70) and lysosomeassociated membrane protein 2A (LAMP2A) expression. Selonsertib treatment corrected all the phenotypes observed in immortalized human podocytes with reduced SMPDL3b expression.