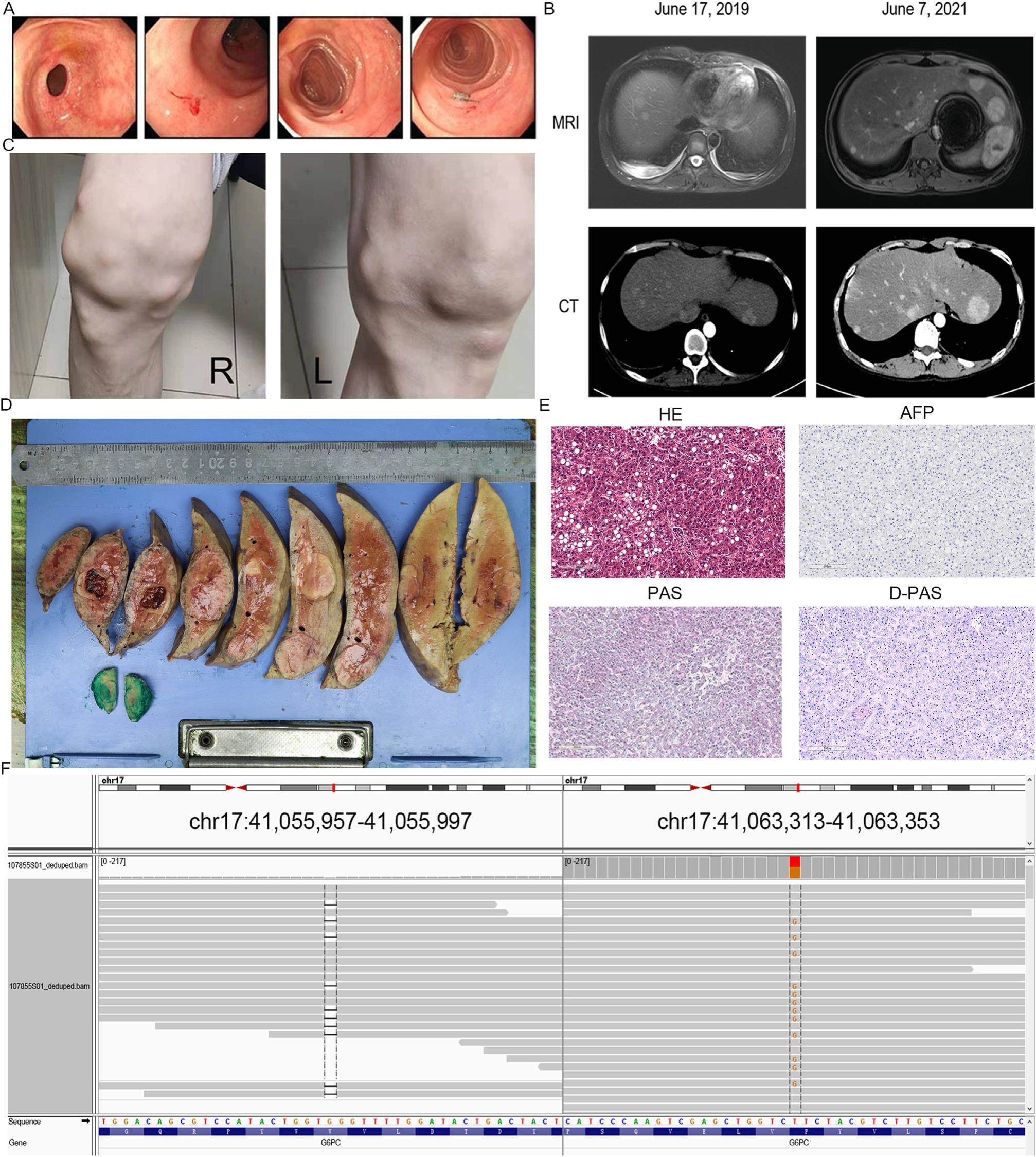
A patient with glycogen storage disease type IA combined with hepatic adenoma: A case report


Glycogen storage disease (GSD) is a rare autosomal recessive disease by abnormal accumulation of intracellular glycogen. Mutations in genes encoding G-6-P or G-6-Pase lead to dysfunction of the body's glycogen metabolism. Without adequate metabolic treatment, patients with GSD can die during infancy or childhood from severe hypoglycemia and acidosis. The patient's symptoms generally achieve remission during adolescence, except in rare cases when cirrhosis of the liver or myopathy occurs. Once GSD is identified in adults, the patients are often accompanied by many complications, such as fasting hypoglycemia, hyperlipidemia, hyperlactatemia and hyperuricemia. In most cases, these complications may mask the patient's primary disease. At present, there are more than 14 types of GSD. The details were presented in. It's worth noting that Glycogen storage disease type IA (GSD-IA) is the most prevalent subtype and represents approximately 80% of GSD-I cases. It's characterized by a deficiency of glucose-6 phosphatase (G-6-P), a key enzyme in glycogen metabolism. However, G-6-Pase deficiency blocked the normal pathway of glycogenolysis and glycogen is accumulated excessively in the liver or muscle. This is why the patients with GSD are typically characterized by hypoglycemia and hepatomegaly. Once the metabolic alternative pathways are activated, the body will develop various complications.