Stabilization of MYC G-quadruplex DNA by ruthenium (II) complex overcomes imatinib resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia cells harboring T315I mutation


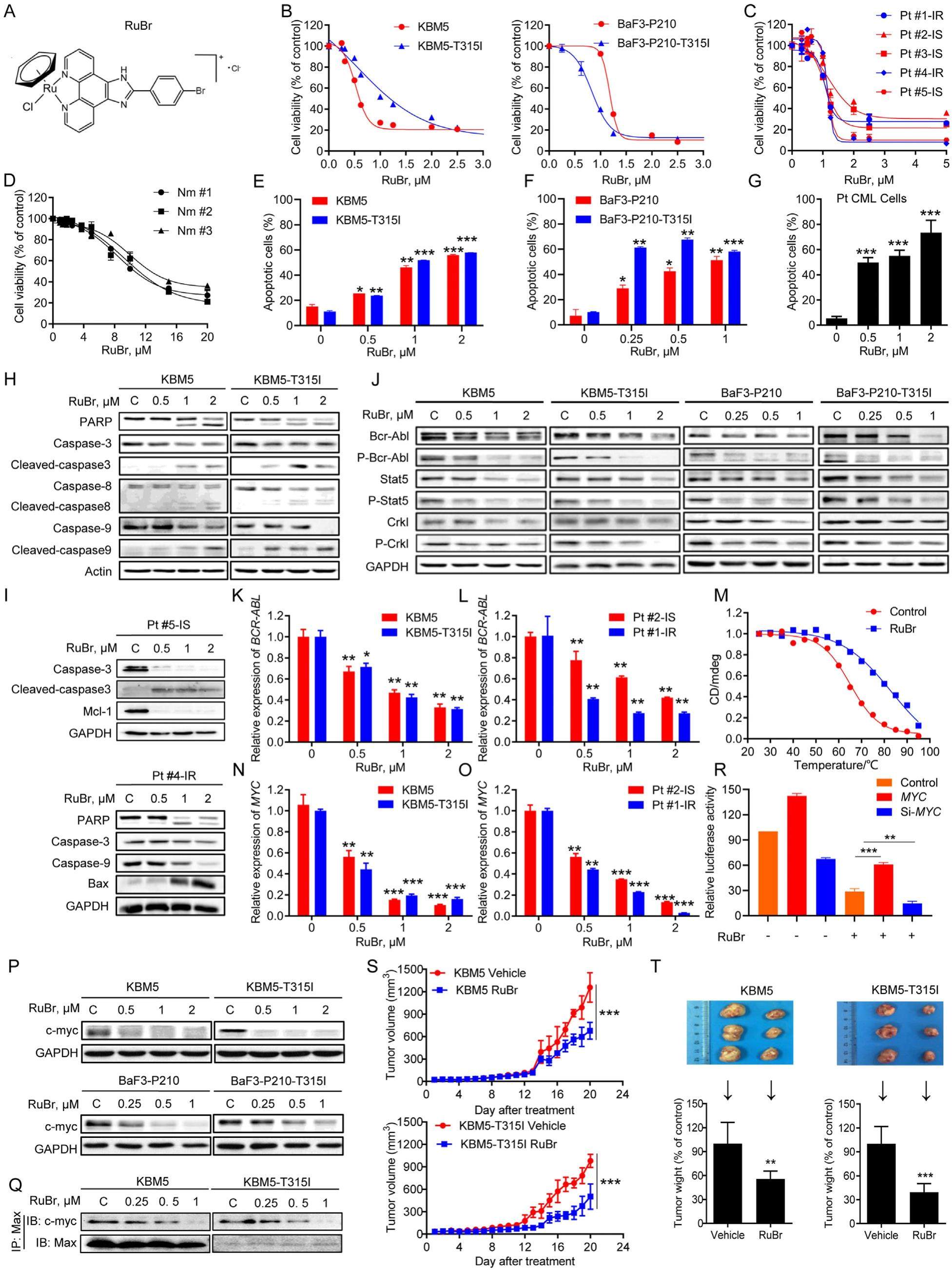
The key pathogenesis of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is the formation of BCR-ABL fusion gene, encoding a 210 kDa Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase, which is crucial for the occurrence and development of CML. Imatinib (IM) is the first targeted anticancer drug approved by FDA for the treatment of CML; however, some patients, especially those in accelerated phase and blastic phase, develop primary or secondary drug resistance to IM. Particularly, the most challenging resistance is caused by T315I mutation of Bcr-Abl, which represents approximately 15%-20% of all acquired mutations and renders cell resistant to a variety of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Thus, there is an urgent need to develop novel strategiestoovercomeBcr-AblT315I-meidatedIM resistance.