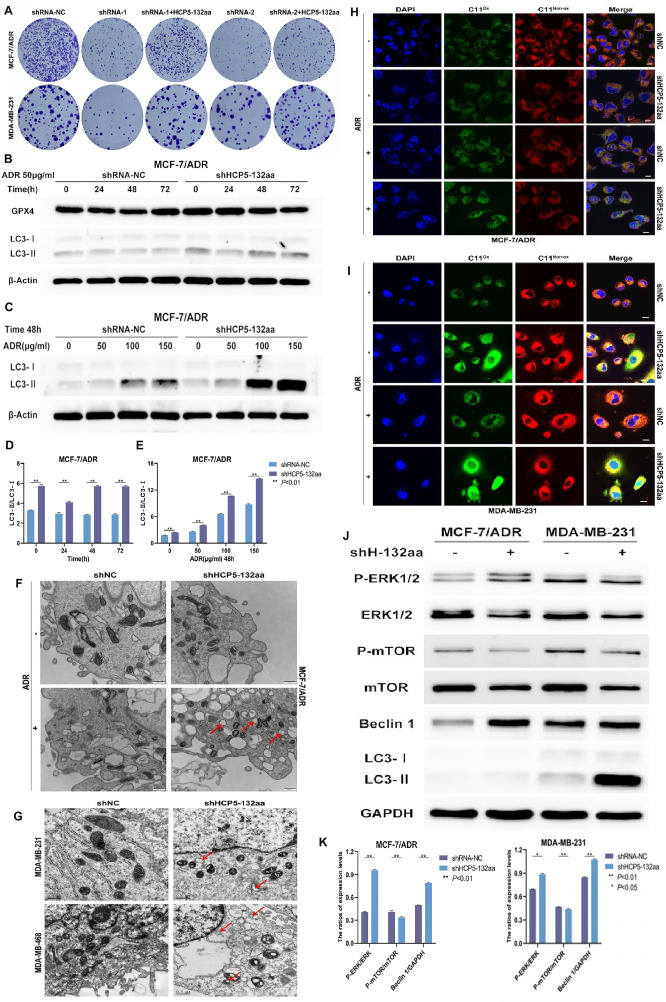
LncRNA HCP5-encoded protein contributes to adriamycin resistance through ERK/mTOR pathway-mediated autophagy in breast cancer cells


Adriamycin (ADR), also known as doxorubicin, is an anthracycline anticancer drug and a chemotherapeutic drug commonly used in breast cancer treatments.1 However, breast cancer patients can gradually become tolerant to chemotherapy. Therefore, improving the curative effect of ADR remains an urgent problem to be solved. Autophagy is a complex catabolic process; normal living cells break down damaged organelles or aggregated molecules and absorb energy to maintain homeostasis through autophagy. When autophagy dysfunction occurs, it will inevitably cause cell death. Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) is a transcript longer than 200 nucleotides in length.2 As a human-specific gene, lncRNA human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen complex P5 (HCP5) is located in the major histocompatibility complex class Ⅰ region and can generate a transcript of approximately 2.5 kb. There is also a relationship between HCP5 and drug resistance.3