Hsa_circ_0007099 and PIP4K2A coexpressed in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with clinical significance


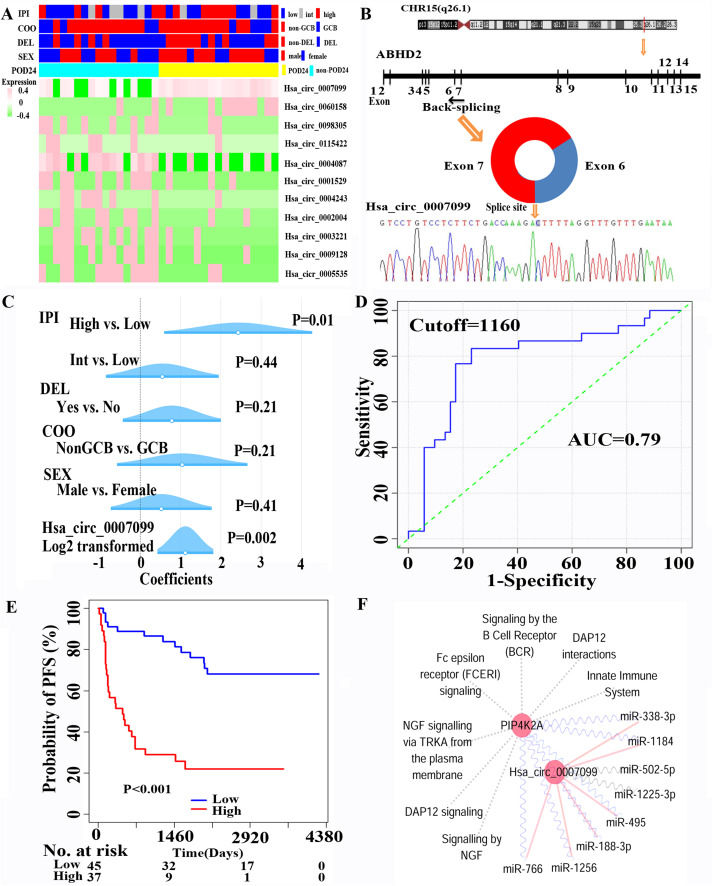
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common subtype of B-cell lymphoma in adult patients. Due to the clinical and molecular heterogeneity of DLBCL patients, robust biomarkers in clinical practice are still required. Clinically, the international prognostic index (IPI) was considered the most well-established predictor. Molecularly, mRNA expression and genetic subtypes were regarded as useful biomarkers. However, the prognostic potential of circRNA expression in DLBCL patients is still unclear. CircRNAs are more stable than linear mRNAs. Due to their richness, stability, and tissue specificity, circRNAs should have a potential utility as cell-free biomarkers.1,2 Notably, B-cells have specific circRNA markers compared with T-cells. Additionally, circRNA expression profiles can distinguish different B-cell malignancies.3 Besides, circRNAs are expressed in higher amounts in some diseases than their corresponding linear mRNAs. Based on these studies, we used RNA sequencing to search for circRNAs related to disease progression and identified hsa_circ_0007099 as one of the significant predictors. Furthermore, the regulatory pathway of hsa_circ_0007099 was constructed in in silico analysis and validated in in vitro cellular experiments.