Epinephrine promotes tumor progression and M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages by regulating the TRIM2- NF-κB pathway in colorectal cancer cells


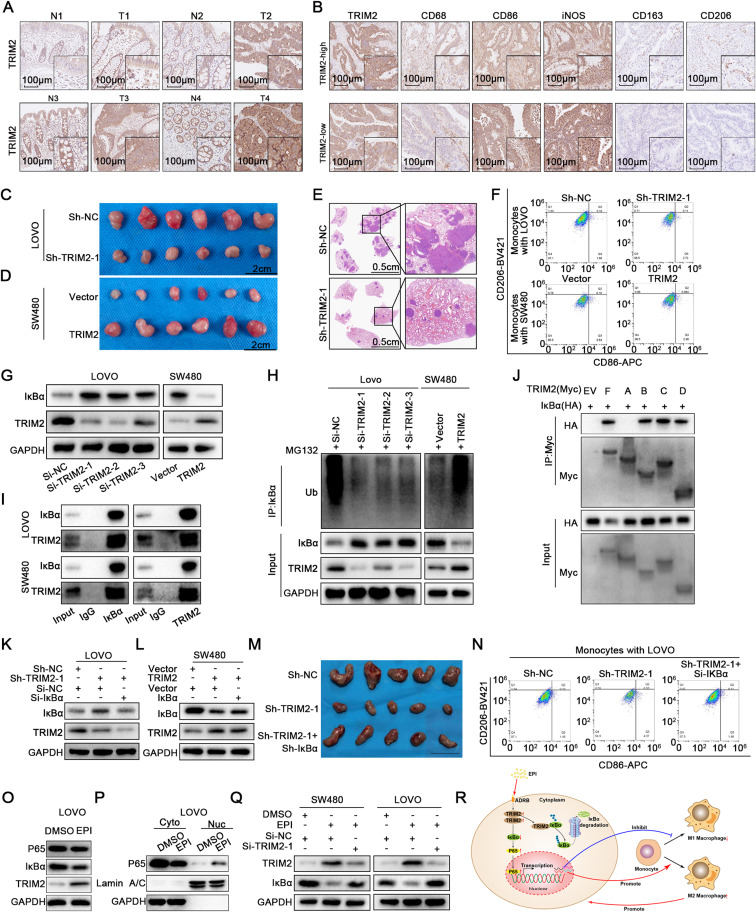
Tumor-associated inflammation is an important component of the tumor microenvironment, and an important factor affecting tumor progression. In the tumor microenvironment, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) receive different stimuli and can be polarized into classically activated M1 macrophages and alternatively activated M2 macrophages. Many studies have indicated that the polarization of TAMs is closely related to tumor progression. M2-polarized TAMs have been highly correlated with tumor metastasis, angiogenesis, and poor prognosis, whereas M1-polarized TAMs suppress tumor development. Tumors with higher densities of M2 macrophages and lower densities of M1 macrophages have poor clinical outcomes.1 In terms of molecular mechanism, M2-polarized TAMs can produce various cytokines required for tumor cell growth and angiogenesis, including TGF-β, VEGF, and EGF.2 In addition, M2-polarized TAMs can inhibit humoral and cellular immunity to cancer cells through various pathways, maintain tumor cells in an immune tolerance state, and evade clearance by the body. Tumor cells can regulate TAM polarization toward the M1 or M2 phenotype by regulating the tumor microenvironment and releasing cytokines.3 TRIM family proteins have been reported to be closely related to immune regulation, inflammation, and tumorigenesis.4 In our previously published research, we found that epinephrine (Epi) could promote the progression of colorectal cancer (CRC) by promoting the expression of TRIM2.5 However, the immunomodulatory role of TRIM2 in CRC is still unknown. In this study, we found that Epi promotes tumor proliferation, migration, and M2 polarization of TAMs by up-regulating TRIM2 expression in CRC cells. TRIM2 expression is closely related to CRC progression. TRIM2 promotes the development of CRC by promoting the ubiquitination and degradation of IκBα. TRIM2 can also promote M2 polarization of TAMs, which can further promote the progression of CRC. Collectively, targeting the Epi/TRIM2 signaling pathway might be a promising treatment option for CRC.