Transcriptomic analysis reveals that NIBAN1 overexpression is associated with BRAFV600E mutation and increases the aggressiveness of thyroid cancer


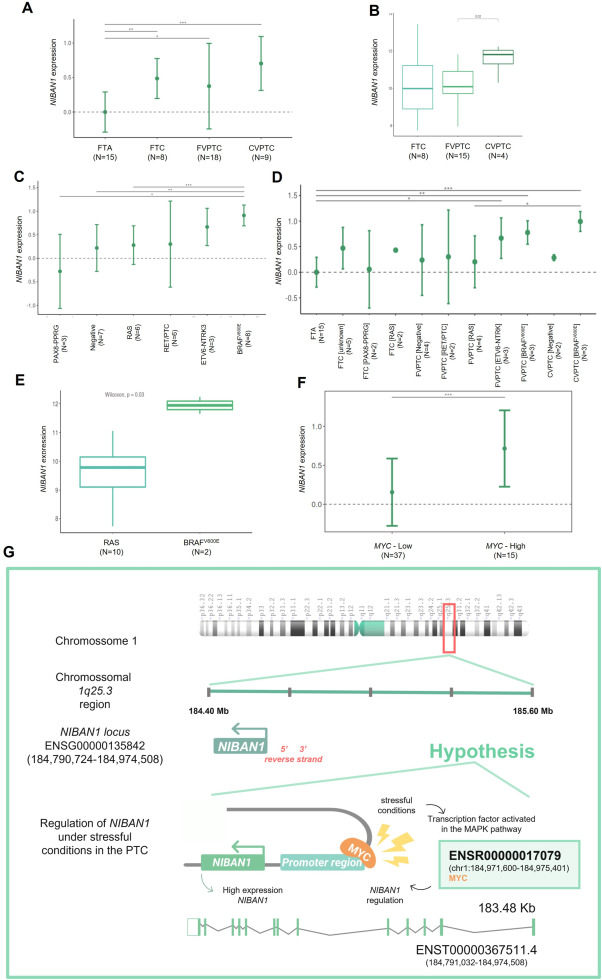
NIBAN1 overexpression has been reported in a wide range of thyroid carcinoma subtypes, and in other cancers, while it is not expressed in thyroid benign lesions and normal thyroid.1, 2, 3 However, the mechanism associated with its expression and prognostic value remains unclear. In this study, six independent cohorts were enrolled, in which NIBAN1 expression was evaluated. A total of 583 patients with thyroid tumors, 326 patients with skin cancers, 293 patients with colorectal carcinoma, and 189 patients with lung carcinoma were analyzed. Our study demonstrates, for the first time, that NIBAN1 expression varied according to thyroid tumor subtypes, presence of BRAFV600E mutation, worse clinical features, and aggressive phenotype. Remarkably, the data suggest that BRAFV600E mutation might influence NIBAN1 expression in an MYC-dependent manner during the thyroid carcinogenic process. Furthermore, NIBAN1 expression was predicted to be associated with stress-induced transcription/translation. In summary, our findings suggested that NIBAN1 expression could be used not only to help preoperative diagnosis of a thyroid nodule but also may have prognostic implications.