NKCC1 and NKCC2: The pathogenetic role of cation-chloride cotransporters in hypertension


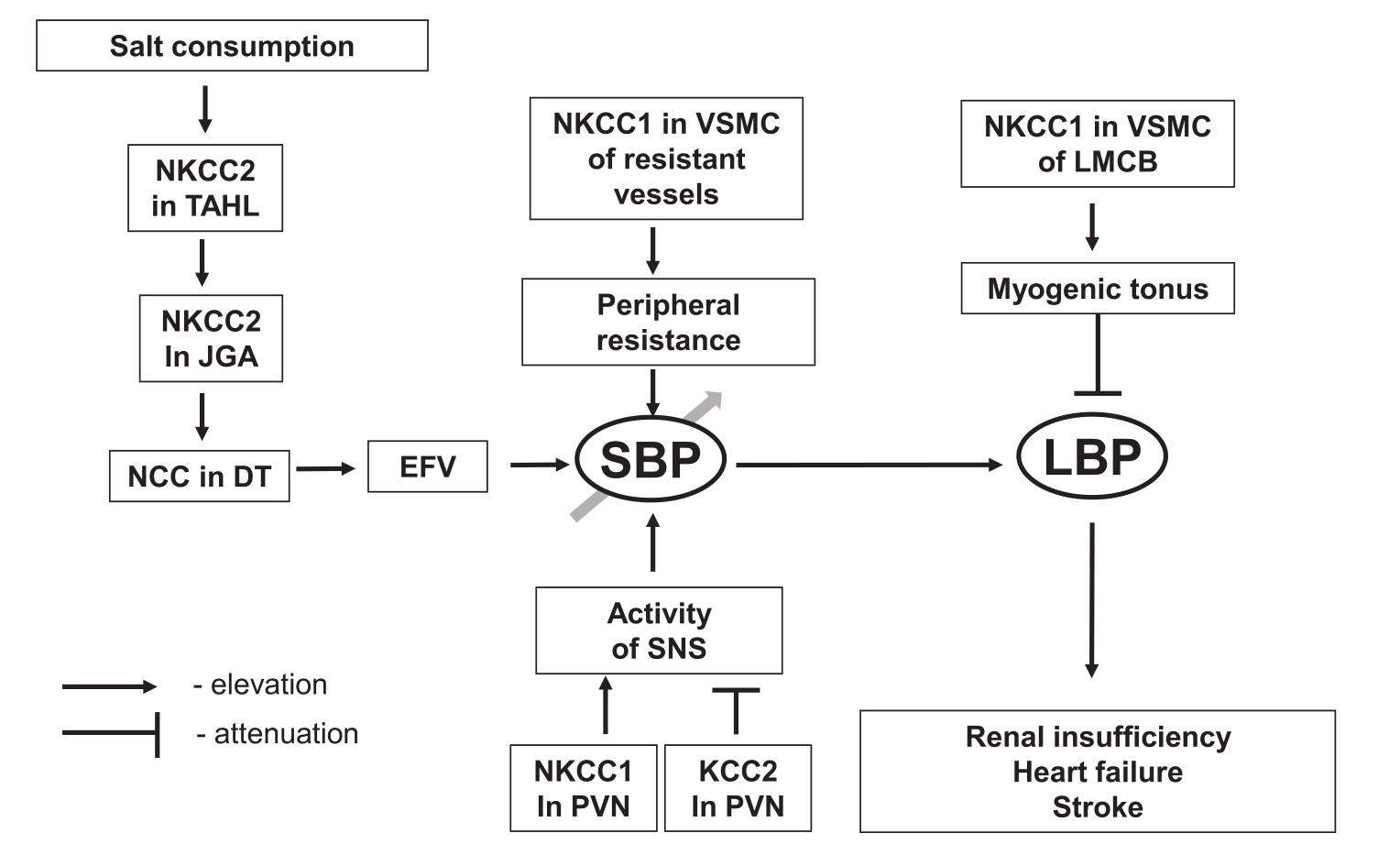
This review summarizes the data on the functional significance of ubiquitous (NKCC1) and renal-specific (NKCC2) isoforms of electroneutral sodium, potassium and chloride cotransporters. These carriers contribute to the pathogenesis of hypertension via regulation of intracellular chloride concentration in vascular smooth muscle and neuronal cells and via sensing chloride concentration in the renal tubular fluid, respectively. Both NKCC1 and NKCC2 are inhibited by furosemide and other high-ceiling diuretics widely used for attenuation of extracellular fluid volume. However, the chronic usage of these compounds for the treatment of hypertension and other volume-expanded disorders may have diverse side-effects due to suppression of myogenic response in microcirculatory beds.