Protein phosphatase 6 (Pp6) is crucial for regulatory T cell function and stability in autoimmunity


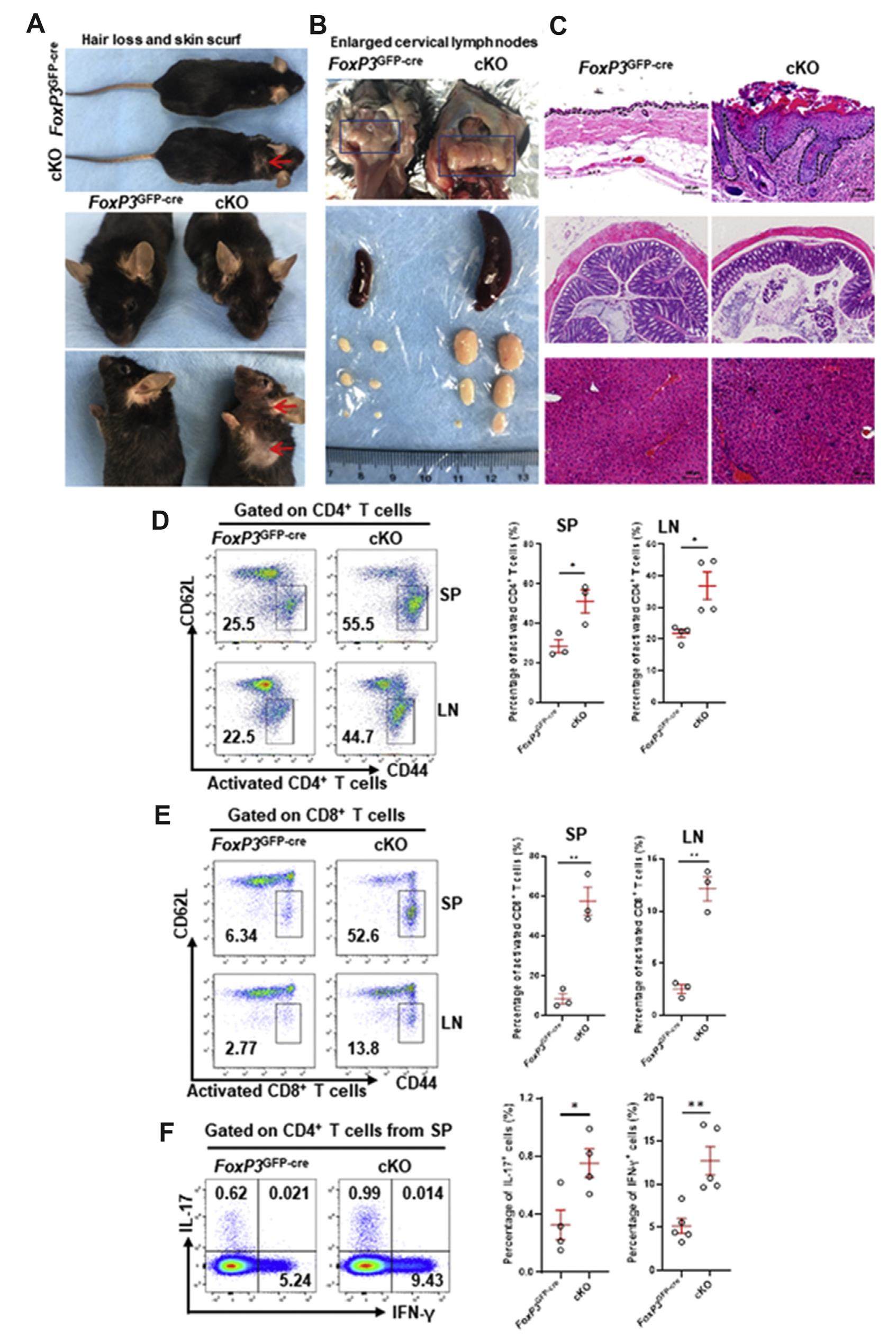
Regulatory T (Treg) cells constitute a dynamic population that is critical in autoimmunity. Treg cell therapies for autoimmune diseases are mainly focused on enhancing their suppressive activities. However, recent studies demonstrated that certain inflammatory conditions induce Treg cell instability with diminished FoxP3 expression and convert them into pathogenic effector cells. Therefore, the identification of novel targets crucial to both Treg cell function and plasticity is of vital importance to the development of therapeutic approaches in autoimmunity. In this study, we found that conditional Pp6 knockout (cKO) in Treg cells led to spontaneous autoinflammation, immune cell activation, and diminished levels of FoxP3 in CD4+ T cells in mice. Loss of Pp6 in Treg cells exacerbated two classical mouse models of Treg related autoinflammation. Mechanistically, Pp6 deficiency increased CpG motif methylation of the FoxP3 locus by dephosphorylating Dnmt1 and enhancing Akt phosphorylation at Ser473/Thr308, leading to impaired FoxP3 expression in Treg cells. In summary, our study proposes Pp6 as a critical positive regulator of FoxP3 that acts by decreasing DNA methylation of the FoxP3 gene enhancer and inhibiting Akt signaling, thus maintaining Treg cell stability and preventing autoimmune diseases.