A novel heterozygous SF1/NR5A1 gene variant causes 46,XY DSD-gonadal dysgenesis with hypergonadotropic hypogonadism without adrenal insufficiency


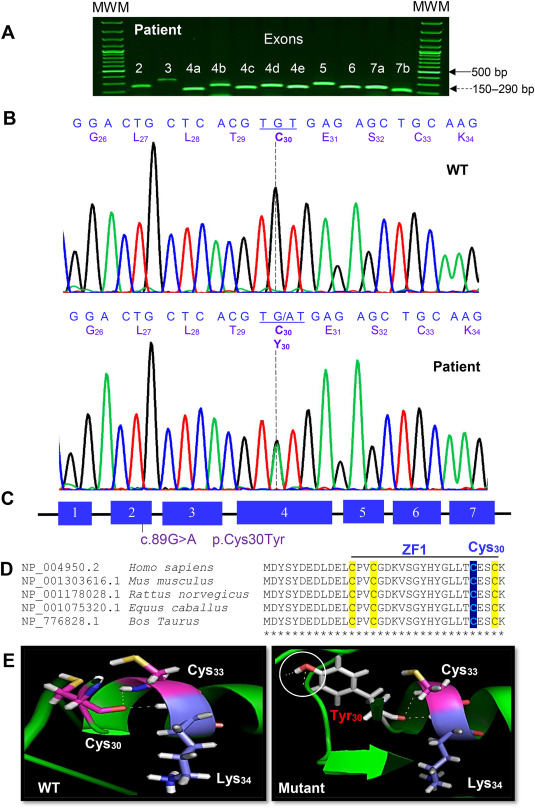
Steroidogenic factor 1 (SF1/NR5A1; nuclear receptor subfamily 5 group A member 1) is an essential orphan protein involved in gonadal embryogenesis, sex determination, and reproductive endocrinology.1 Furthermore, NR5A1 is a transcription factor that regulates a number of target genes [e.g., SRY (sex determining Region Y), SOX9 (SRY-box transcription factor 9), GATA4 (GATA binding protein 4), AMH (anti-Mullerian hormone), STAR (steroidogenic acute regulatory protein), and CYP11A1 (cytochrome P450 family 11 subfamily A member 1)] crucial to reproductive biology. Several human NR5A1 gene variants have been associated with 46,XY disorders of sex development (DSD), a congenital condition in which the gonadal or anatomical sex is atypical.2 While NR5A1's role as a transcription factor essential to adrenal development is supported by several in vitro and in vivo experiments in knockout mouse models, to date, adrenal insufficiency in humans due to NR5A1 gene mutations is extremely rare.3 In this regard, next-generation sequencing approaches are a powerful tool in defining population genetics of rare diseases and allow more focused clinical genetic screening programs to be established. Therefore, the molecular etiology of this genetic steroid disorder is still unknown. Likewise, genomic analyses performed in our laboratory have revealed several non-synonymous mutations in NR3C4/AR (androgen receptor) and SRD5A2 (steroid 5 alpha-reductase 2) genes in patients with 46,XY DSD.4,5 We also showed that mutations of the NR3C4/AR protein reduced or nulled responses to androgens, testosterone, and dihydrotestosterone. Moreover, mutations in the SRD5A2 protein affect its enzymatic activity due to erroneous interactions between amino acid residues, the substrate testosterone, or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate. Here, a novel NR5A1 gene variant is described in a Mexican patient raised as a female due to her phenotype. This female patient has a 46,XY karyotype, undescended atrophied testes, and hypergonadotropic hypogonadism. This study identified a novel heterozygous missense NR5A1 variant (c.89G > A, p.Cys30Tyr) in the first zinc finger of the DNA-binding domain that explains the 46,XY-female phenotype to a genetic condition, and adds to the variety of 46,XY DSD-causing mutations that impair the development of gonadal and phenotypic sex.